Antibiotic Resistance: A Silent Threat
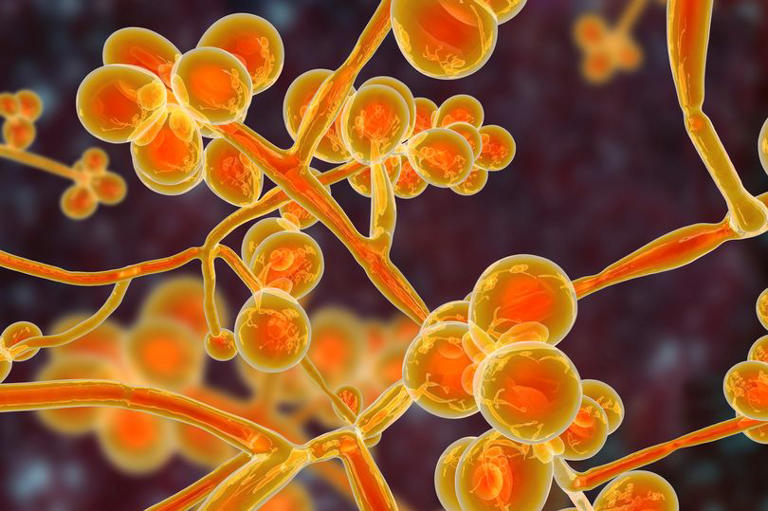
Antibiotic resistance is a growing global health crisis that occurs when bacteria develop the ability to resist the effects of antibiotics. This means that these drugs become less effective in treating infections, making them more difficult to cure.
© Getty
What is Antibiotic Resistance?
Antibiotic resistance happens when bacteria change over time and no longer respond to antibiotics. This can occur naturally, but it’s often accelerated by the overuse and misuse of antibiotics. When bacteria become resistant, they can cause serious infections that are harder to treat, leading to longer illnesses, increased healthcare costs, and even death.
How Does Antibiotic Resistance Happen?
Antibiotic resistance is a complex process that involves several factors:
- Overuse of Antibiotics: When antibiotics are used too often or for unnecessary reasons, it creates an environment where bacteria can develop resistance.
- Misuse of Antibiotics: Not taking antibiotics as prescribed, such as stopping treatment early or not taking the full course, can also contribute to resistance.
- Antibiotic Use in Agriculture: Antibiotics are used in agriculture to treat animal infections and promote growth. However, this can lead to the development of resistant bacteria that can spread to humans.
The Impact of Antibiotic Resistance
Antibiotic resistance has far-reaching consequences:
- Serious Infections: Resistant bacteria can cause severe infections that are difficult to treat, such as pneumonia, bloodstream infections, and urinary tract infections.
- Increased Healthcare Costs: Treating resistant infections often requires more intensive care, longer hospital stays, and more expensive medications.
- Global Health Threat: Antibiotic resistance is a global problem that affects people of all ages and backgrounds. It can lead to increased mortality rates and reduced quality of life.
Preventing Antibiotic Resistance
To combat antibiotic resistance, it’s crucial to take the following steps:
- Use Antibiotics Wisely: Only use antibiotics when necessary and follow your doctor’s instructions carefully.
- Complete the Full Course: Finish the entire course of antibiotics, even if you start to feel better.
- Prevent Infections: Practice good hygiene, such as washing your hands frequently and staying up-to-date on vaccinations.
- Support Research and Development: Encourage investment in research to develop new antibiotics and innovative treatments.
- Advocate for Responsible Antibiotic Use: Raise awareness about the dangers of antibiotic resistance and promote responsible use in both human and animal health.
By understanding the causes and consequences of antibiotic resistance, we can take steps to protect ourselves and future generations. Let’s work together to combat this silent threat and ensure the continued effectiveness of antibiotics.
Related:
Mercury Contamination in Tuna: 7 Shocking Dangers You Need to Know!