China Far Side Moon Landing
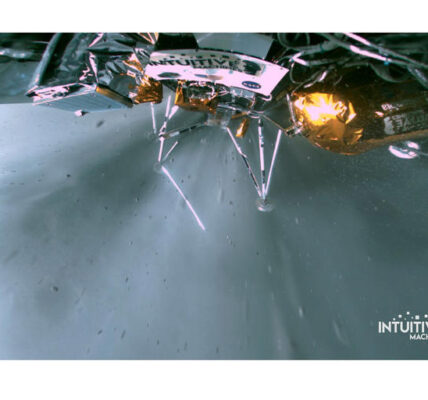
China far side moon landing marks a groundbreaking achievement in space exploration, showcasing China’s growing capabilities and ambitions. On Sunday, a Chinese spacecraft successfully landed on the moon’s far side to collect soil and rock samples. This mission could provide critical insights into the differences between the less-explored far side and the well-known near side of the moon.

© Provided by PA Media
Historic Landing in the South Pole-Aitken Basin
The landing module touched down at 6:23 am Beijing time in the South Pole-Aitken Basin, one of the largest impact craters in the solar system. This mission is the sixth in the Chang’e moon exploration program, named after a Chinese moon goddess. It follows the Chang’e 5 mission, which collected samples from the near side of the moon in 2020.
Mission Objectives and Scientific Goals
The China far side moon landing aims to gather up to two kilograms (4.4 pounds) of surface and underground material. The lander is equipped with a mechanical arm and a drill for this purpose. The collected samples will be analyzed to understand the geological differences between the moon’s far side and its near side.
Complex Operations and Technological Challenges
Missions to the moon’s far side are particularly challenging. The far side does not face Earth, making direct communication impossible. To overcome this, a relay satellite is used to maintain contact between the lander and mission control. Additionally, the rugged terrain of the far side presents fewer flat areas for a safe landing, adding to the mission’s complexity.
Sample Collection and Return Plan
Once the samples are collected, an ascender atop the lander will transport them to a module orbiting the moon. This module will then transfer the samples to a re-entry capsule. The capsule is expected to return to Earth around June 25, landing in China’s Inner Mongolia region.
Growing Rivalry in Space Exploration
The China far side moon landing is part of a broader context of increasing competition in space exploration. China’s space program has made significant strides, including placing its own space station in orbit and regularly sending crews there. The country aims to send astronauts to the moon before 2030, potentially becoming the second nation, after the United States, to achieve this feat.
Comparison with US Space Efforts
The United States, historically the leader in space exploration, has been experiencing delays in its lunar missions. NASA plans to land astronauts on the moon again, targeting a new date of 2026 after pushing back the original timeline. Efforts to use private sector rockets, such as those developed by Boeing and SpaceX, have faced setbacks. Recently, Boeing’s planned astronaut flight was delayed due to last-minute computer issues. Additionally, a Japanese billionaire canceled his planned lunar orbit mission because of uncertainties with SpaceX’s mega-rocket development.
Significance of the China Far Side Moon Landing
The China far side moon landing is a significant achievement, highlighting the country’s growing prowess in space technology. By successfully landing on the moon’s far side and planning to bring back samples, China demonstrates its capability to conduct complex space missions. This achievement not only advances scientific knowledge but also enhances China’s standing in the global space race.
Future Prospects and Global Implications
Looking ahead, the China far side moon landing sets the stage for more ambitious goals. China’s lunar program includes plans to establish a research base on the moon and send crewed missions. These endeavors will likely accelerate the competition with the United States and other nations, such as Japan and India, who are also advancing their space programs.

© Provided by PA Media
Challenges and Opportunities in Lunar Exploration
The rugged and less-explored far side of the moon offers unique scientific opportunities. By studying the samples collected from this region, scientists hope to gain new insights into the moon’s formation and geological history. The China far side moon landing is expected to contribute significantly to this body of knowledge, potentially leading to new discoveries.
China’s Long-term Space Strategy
China’s commitment to its space program is evident in its systematic approach and long-term planning. The Chang’e missions are part of a broader strategy that includes developing space infrastructure, conducting deep space exploration, and fostering international collaborations. The China far side moon landing is a crucial step in this comprehensive plan.
Conclusion
The China far side moon landing represents a landmark achievement in space exploration. By successfully landing on the moon’s far side and preparing to return samples to Earth, China demonstrates its growing capabilities and ambitions. This mission not only advances our understanding of the moon but also underscores the increasing competition in space exploration. As China continues to pursue its space goals, the global landscape of space exploration is set to become even more dynamic and competitive.
ALSO READ:
Phobos Captured Comet Theory: 7 Astonishing Discoveries!