Recent Lunar Volcanic Activity Discovery: New research reveals that volcanic eruptions on the Moon occurred much more recently than previously thought, continuing until about 120 million years ago, during the age of dinosaurs. Learn more about this groundbreaking finding and its implications.

© Canva
Recent Lunar Volcanic Activity Discovery: A New Look at the Moon’s Volcanic History
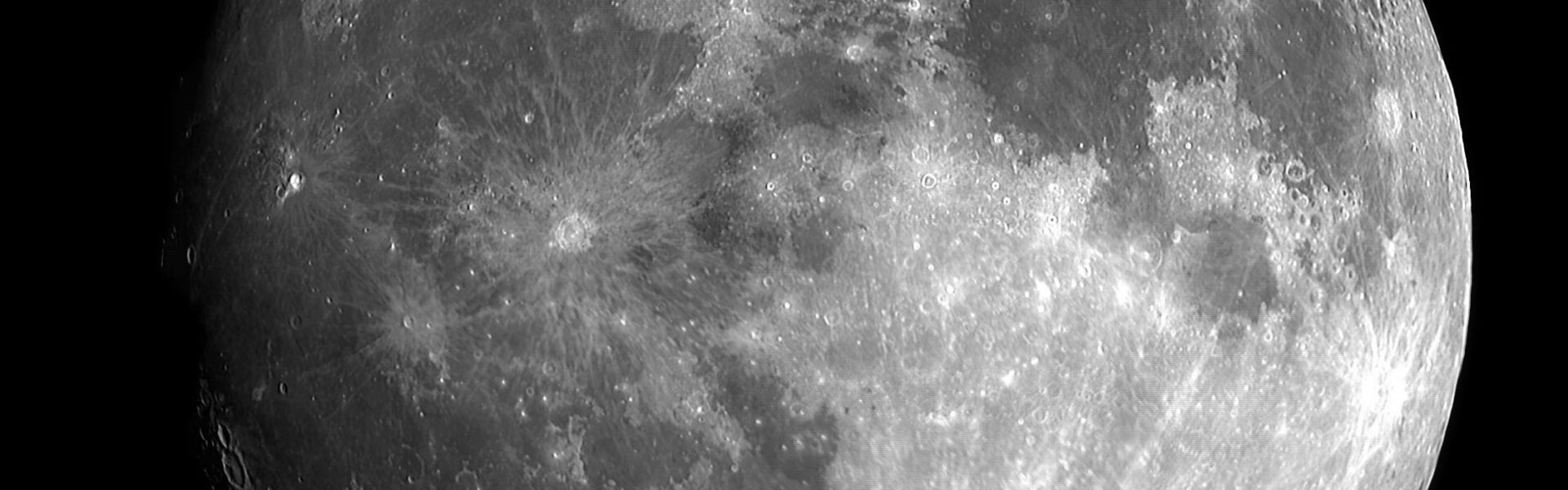
Recent Lunar Volcanic Activity Discovery is shaking up our understanding of the Moon’s volcanic past. For decades, scientists believed the Moon’s volcanic activity had ended billions of years ago. However, new research has uncovered surprising evidence that lunar volcanoes may have been active as recently as 120 million years ago, a time when dinosaurs roamed the Earth.
The Breakthrough Discovery
The game-changing evidence comes from three tiny glass beads collected by China’s Chang’e 5 mission, which brought Moon samples back to Earth in 2020. These beads, each smaller than a pinhead, hold clues about volcanic activity on the Moon. The chemical composition of these beads suggests that lunar volcanoes were active much later than scientists previously thought.
Before this discovery, analyses of lunar rock samples from earlier missions, including those from NASA’s Apollo program and Soviet spacecraft, indicated that volcanic activity had ceased about 2 billion years ago. Some estimates even pushed this timeline back to 4 billion years ago. But the findings from the Chang’e 5 mission suggest a more recent volcanic history, challenging long-held beliefs about the Moon’s cooling process.
How Glass Beads Reveal Volcanic Activity
The lunar glass beads are a significant piece of evidence. They form when molten lunar material cools rapidly after a volcanic eruption or meteorite impact. The presence of these beads with signs of volcanic origin indicates that the Moon’s surface was still experiencing volcanic activity long after the expected cooling period.
Julie Stopar, a senior staff scientist with the Lunar and Planetary Institute, commented on the discovery. The new findings are a notable shift from previous estimates and provide a fresh perspective on the Moon’s volcanic history.
Implications for Lunar Geology
The Recent Lunar Volcanic Activity Discovery has important implications for our understanding of the Moon and other small celestial bodies. The research highlights that the Moon remained volcanically active far longer than previously believed. This discovery opens up new questions about how long small planets and moons can stay volcanically active.
The study analyzed around 3,000 glass beads from the Moon’s surface, identifying three that showed signs of coming from a volcanic source. This is the first direct evidence supporting the idea of recent volcanic activity on the Moon, though further research is needed to fully confirm these findings and understand their implications.
The Role of Previous Research
Earlier images from NASA’s Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, taken in 2014, hinted at the possibility of more recent volcanic activity. These images showed features on the Moon’s surface that could be related to volcanic processes. The new research provides physical evidence to support these earlier observations, reinforcing the idea that the Moon’s volcanic history is more complex than previously understood.
Future Research Directions
The discovery of recent volcanic activity on the Moon inspires further studies to explore how such activity could occur on a body that was thought to have cooled long ago. Scientists will need to conduct additional research to validate the findings and understand the mechanisms that allowed the Moon to remain volcanically active for so long.
Understanding the volcanic history of the Moon also has implications for other celestial bodies in our solar system. It can help scientists learn more about the thermal evolution of moons and small planets, shedding light on their geological history and potential for volcanic activity.
Conclusion
The Recent Lunar Volcanic Activity Discovery is a groundbreaking revelation that challenges our previous understanding of the Moon’s volcanic history. By analyzing tiny glass beads from the Chang’e 5 mission, scientists have uncovered evidence that lunar volcanoes were active as recently as 120 million years ago. This new information prompts a reevaluation of the Moon’s cooling timeline and offers new insights into the volcanic processes on small celestial bodies.
As researchers continue to study these findings, we can expect a deeper understanding of the Moon’s geological history and the volcanic activity on other planets and moons. This discovery not only enriches our knowledge of the Moon but also inspires future research into the dynamic processes shaping our solar system.
Related:
Hubble Tension Controversy: 5 Stunning Discoveries Redefining the Universe