Understanding the Type 2 Diabetes Epidemic: What You Need to Know
Explore the growing prevalence of Type 2 diabetes and learn how it affects individuals, from symptoms to prevention strategies. Discover actionable steps to manage this metabolic disorder effectively.
Type 2 Diabetes Epidemic: Unveiling the Reality
In recent years, the prevalence of Type 2 diabetes has surged, marking an alarming trend in public health. This metabolic disorder, characterized by high blood sugar levels, poses significant challenges for individuals and healthcare systems worldwide. Let’s delve into the intricacies of Type 2 diabetes, its impact on health, and practical approaches to tackle this growing epidemic.
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes: A Simple Overview
Type 2 diabetes arises when the body fails to effectively utilize insulin, a hormone crucial for regulating blood sugar levels. This condition doesn’t manifest suddenly but gradually progresses over time. Initially, individuals may experience prediabetes, where blood glucose levels hover above the normal range.
Symptoms of Type 2 diabetes, such as increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, blurred vision, and unintentional weight loss, may not manifest until blood sugar levels soar into the diabetic range. It’s essential to undergo routine screenings to detect prediabetes and Type 2 diabetes early, enabling timely intervention and management.
Factors Contributing to Type 2 Diabetes
Various factors contribute to the development of Type 2 diabetes, including genetics, age, obesity, sedentary lifestyle, and poor dietary habits. While obesity and unhealthy eating patterns are significant contributors, it’s crucial to recognize that not all individuals with Type 2 diabetes are overweight. Genetics, family history, and certain medical conditions also play pivotal roles in predisposing individuals to this condition.
Risks and Complications Associated with Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes poses substantial risks and complications if left unmanaged. Elevated blood sugar levels over time can lead to cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, neuropathy (nerve damage), retinopathy (eye problems), foot complications, and increased susceptibility to infections. Early detection and proactive management are essential for mitigating these risks and improving long-term health outcomes.
Identifying High-Risk Groups
Certain demographic groups face a higher risk of developing Type 2 diabetes. Individuals from South Asian, African-Caribbean, or black African backgrounds, as well as those with a family history of diabetes, are particularly susceptible. Women with a history of gestational diabetes during pregnancy also have an increased risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later in life. Addressing these risk factors through targeted interventions and awareness campaigns is crucial for reducing the burden of Type 2 diabetes within these communities.
 Prevention and Management Strategies
Prevention and Management Strategies
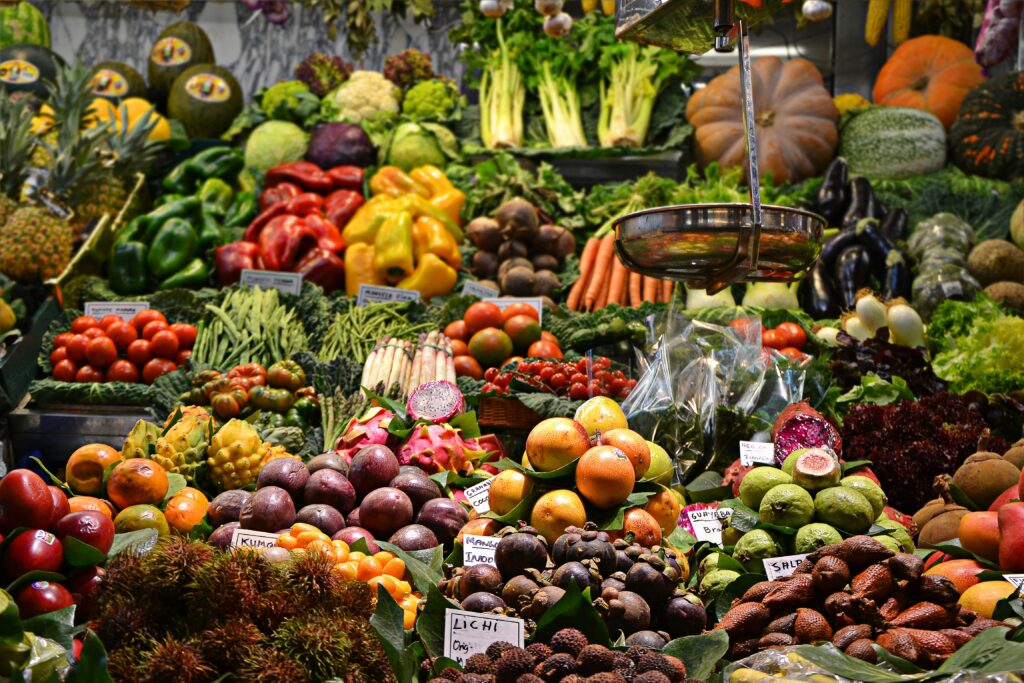
Preventing Type 2 diabetes involves adopting healthy lifestyle practices, including regular physical activity, balanced nutrition, weight management, and smoking cessation. The NHS Diabetes Prevention Programme and similar initiatives worldwide offer evidence-based interventions to help individuals at risk of Type 2 diabetes make sustainable lifestyle changes.
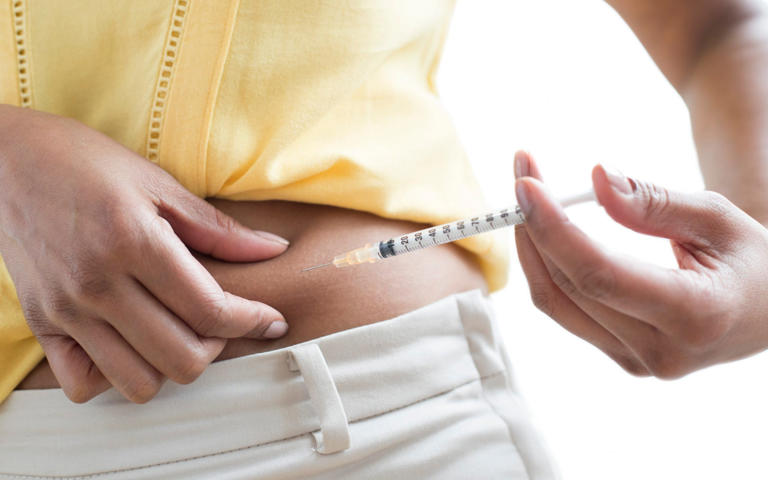
For those already diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes, effective management strategies include medication, dietary modifications, and regular monitoring of blood sugar levels. Newer drug therapies, such as GLP-1 receptor agonists, offer promising options for enhancing glucose control and promoting weight loss in individuals with Type 2 diabetes.

Empowering Individuals Through Education
Education plays a pivotal role in empowering individuals to take charge of their health and well-being. Healthcare professionals, community organizations, and educational institutions must collaborate to raise awareness about Type 2 diabetes risk factors, symptoms, and preventive measures. By equipping individuals with knowledge and resources, we can foster a culture of proactive health management and reduce the incidence of Type 2 diabetes within our communities.
Conclusion: Navigating the Path Towards Better Health
The Type 2 diabetes epidemic underscores the urgent need for collective action and awareness. By understanding the factors contributing to this metabolic disorder and embracing preventive measures, we can curb its prevalence and improve outcomes for individuals affected by Type 2 diabetes. Together, let’s strive to create a healthier future, one where everyone has the tools and support they need to thrive.