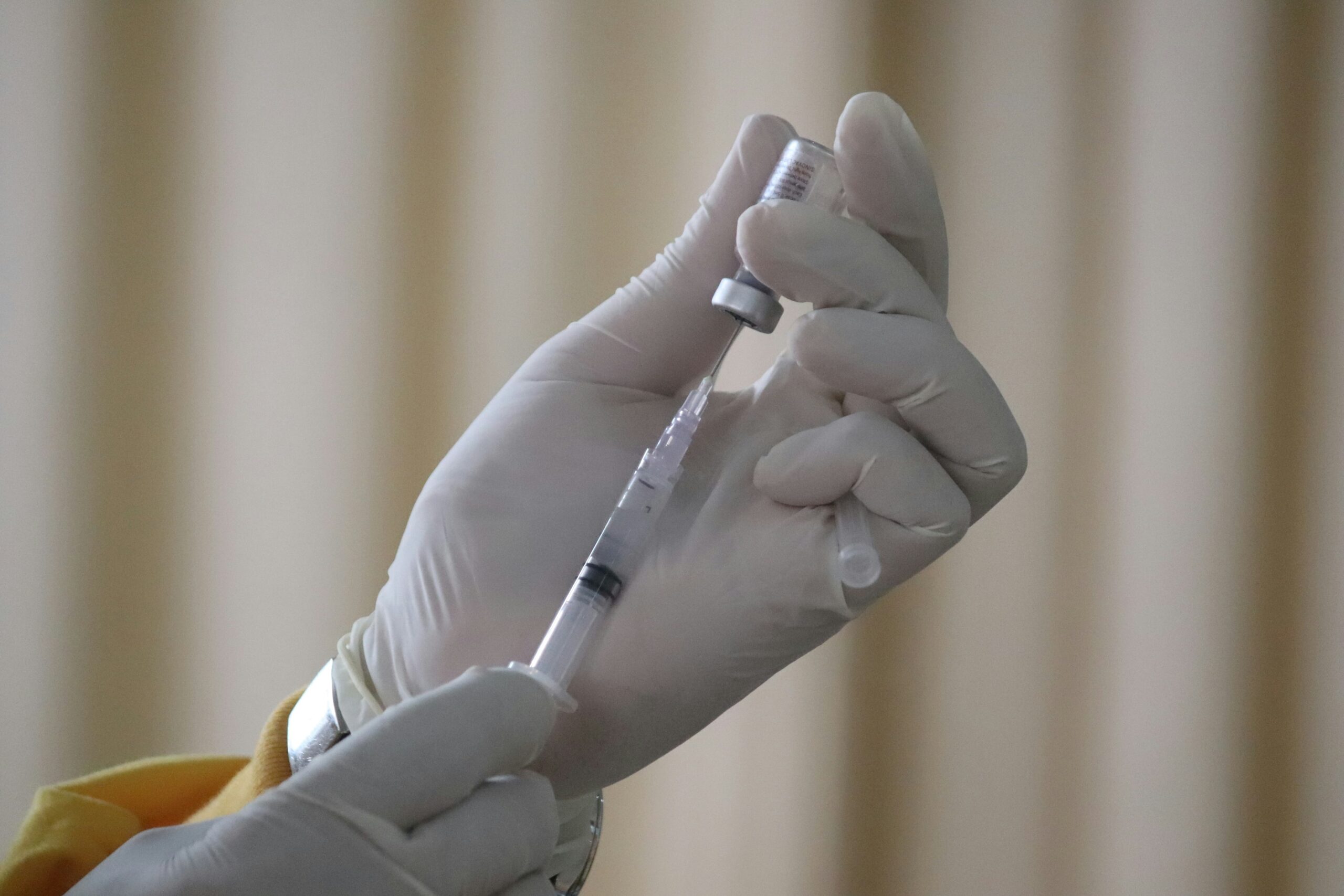
Vaccine-Induced Immune Thrombocytopenia
Vaccine-Induced Immune Thrombocytopenia (VITT) is a rare but serious condition linked to COVID-19 vaccines and certain viral infections. Understanding VITT helps improve vaccine safety and treatment strategies.
© GB News
Vaccine-Induced Immune Thrombocytopenia: Understanding a Rare Condition
Vaccine-Induced Immune Thrombocytopenia (VITT) is a rare but significant complication that has been observed following COVID-19 vaccination. This condition, characterized by severe blood clots and low platelet counts, has prompted extensive research to understand its causes and implications.
As COVID-19 spread globally in 2020, mass vaccination became a crucial strategy to control the virus. Over 13.5 billion doses of COVID-19 vaccines have been administered worldwide, saving countless lives. Despite the success of these vaccines, a very small number of recipients experienced VITT, particularly with adenoviral vector-based vaccines, which use a harmless virus to deliver genetic instructions to our cells.
What is Vaccine-Induced Immune Thrombocytopenia?
Vaccine-Induced Immune Thrombocytopenia (VITT) involves the formation of dangerous blood clots in various parts of the body. This occurs due to an abnormal immune response where the body produces antibodies against platelet factor 4 (PF4), a protein involved in blood clotting. These antibodies trigger platelet activation, leading to clot formation and a drop in platelet count.
Link Between VITT and Adenovirus Infections
Recent research by an international team, including scientists from Flinders University, has uncovered a surprising connection between VITT and natural adenovirus infections, which cause common colds. Studies in 2023 revealed that some individuals developed a disorder similar to VITT after natural adenovirus infection, with the same PF4 antibodies involved. This suggests a shared mechanism between vaccine-induced and infection-induced cases.
Genetic Factors and Molecular Mechanisms
The researchers identified a genetic risk factor related to an antibody gene called IGLV3.21*02, which predisposes individuals to producing the harmful PF4 antibodies. By cracking the molecular code of these antibodies, scientists gained insights into the common pathways that lead to VITT in both vaccine-related and infection-related cases.
Implications for Vaccine Development and Safety
Understanding the genetic and molecular basis of Vaccine-Induced Immune Thrombocytopenia (VITT) has important implications for vaccine development. By identifying the common triggering factors and genetic predispositions, researchers can improve the safety of vaccines and develop strategies to prevent or treat VITT. This research highlights the need for continuous monitoring and adaptation in vaccine technology to ensure public health safety.
Vaccine-Induced Immune Thrombocytopenia: Clinical Implications
For healthcare providers, recognizing and managing VITT is crucial. The condition, although rare, requires prompt diagnosis and treatment. The findings from this research can inform clinical guidelines and enhance patient care by providing a better understanding of the risk factors and mechanisms involved.

© GB News
The Importance of Vaccination Despite Risks
While Vaccine-Induced Immune Thrombocytopenia (VITT) is a serious condition, it is essential to remember that it is extremely rare. Vaccines have been instrumental in reducing severe illness and deaths caused by COVID-19. Regulatory agencies, such as the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) in the UK, continuously review vaccine safety to ensure public health.
Encouraging Continued Vaccination Efforts
As COVID-19 remains a global concern, vaccination continues to be a critical tool in managing the pandemic. Public health authorities, including NHS England, urge at-risk groups to stay up-to-date with their COVID-19 vaccinations. This includes individuals over 75, those with weakened immune systems, and residents of older adult care homes. Continued vaccination efforts help protect vulnerable populations and control the spread of the virus.
Future Directions in Vaccine Research
The ongoing research into Vaccine-Induced Immune Thrombocytopenia (VITT) will pave the way for safer vaccines and improved treatments. By understanding the molecular and genetic factors involved, scientists can design vaccines that minimize the risk of rare complications like VITT. This research also contributes to broader knowledge about immune responses and autoimmune disorders.
Conclusion
Vaccine-Induced Immune Thrombocytopenia (VITT) represents a rare but important area of study in the context of COVID-19 vaccination. The discoveries made by researchers offer valuable insights into the mechanisms behind this condition and its connection to natural viral infections. While VITT poses a serious risk to a very small number of individuals, the overall benefits of vaccination in preventing severe COVID-19 far outweigh these risks. Ongoing research and vigilance will continue to enhance vaccine safety and efficacy, ensuring better protection for all.
ALSO READ:
COVID-19 Vaccination: 3 Surprising Dangers You Must Avoid