Asteroid Threat Mitigation: 5 Genius Ways to Safeguard Earth’s Future!
Asteroid Threat Mitigation: Safeguarding Earth from Cosmic Collisions
Explore how NASA and global agencies collaborate to detect and mitigate potential asteroid threats, ensuring the safety of our planet.
Asteroid Threat Mitigation: Safeguarding Earth from Cosmic Collisions
Astronomers and scientists worldwide are working tirelessly to protect our planet from potential asteroid impacts. With the rise of space exploration and technological advancements, NASA and international agencies have established robust systems to detect, monitor, and mitigate asteroid threats.

Understanding the Threat
The first step in mitigating asteroid threats is understanding the potential dangers they pose. NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office leads the charge in identifying asteroids that could potentially collide with Earth. They keep a close eye on approximately 2,300 known asteroids in our solar system, focusing particularly on the 150 that could cause catastrophic events if they were to impact our planet.
Global Collaboration
To address the global nature of asteroid threats, NASA collaborates closely with the International Asteroid Warning Network (IAWN), a coalition of astronomers from around the world. This network ensures that potential threats are identified and assessed collectively, enhancing our ability to respond effectively.
Early Warning Systems
Early detection is critical in mitigating asteroid threats. The IAWN and NASA work together to develop and maintain systems that can identify potential threats decades in advance. By monitoring the trajectories of asteroids and analyzing their characteristics, scientists can assess the likelihood of a collision and take appropriate action.
Coordinated Response
In the event of an imminent asteroid impact, a coordinated response is essential. The IAWN serves as a communication hub, facilitating collaboration between astronomers, space agencies, and governmental organizations. If a consensus is reached regarding the severity of the threat, the United Nations Office of Outer Space Affairs (UNOOSA) becomes involved in coordinating a global response.
 Mitigation Strategies
Mitigation Strategies
NASA is actively exploring various strategies to mitigate asteroid threats. One such strategy involves redirecting the trajectory of an asteroid using spacecraft. In a groundbreaking mission, NASA successfully diverted the course of a space rock by ramming a small spacecraft into it at high speed.
Another proposed method is the use of a “gravity tractor,” where a spacecraft would be deployed to alter the asteroid’s orbit by exerting gravitational forces. While these techniques show promise, their effectiveness depends on early detection and sufficient lead time before a potential impact.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite significant progress in asteroid threat mitigation, challenges remain. Detection capabilities are constantly improving, but there are limitations to how far in advance we can predict potential impacts. If an asteroid is detected only a few months before impact, mitigation efforts may be limited or ineffective.

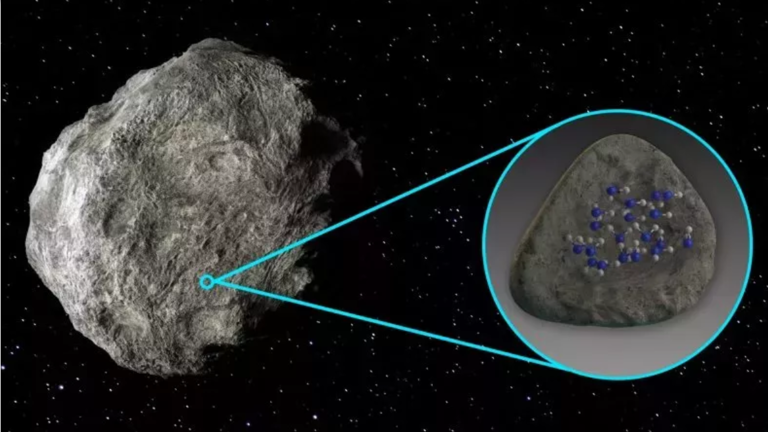
Specific Threats: The Case of Bennu
One asteroid that has garnered attention is Bennu, a small near-Earth asteroid with a 1 in 2,700 chance of colliding with Earth in 2135. While the probability of impact is relatively low, NASA closely monitors Bennu’s trajectory and assesses the potential risk. By identifying and studying asteroids like Bennu, scientists can better understand their behavior and develop targeted mitigation strategies.
Looking Ahead
As technology advances and our understanding of asteroid threats grows, we continue to refine our approach to mitigation. NASA and its partners remain committed to safeguarding Earth from cosmic collisions, employing a combination of early detection, international collaboration, and innovative mitigation techniques.
In conclusion, asteroid threat mitigation is a global endeavor that requires cooperation, diligence, and ingenuity. By working together, we can ensure the safety and security of our planet for generations to come.